Usted está aquí
Featured Article
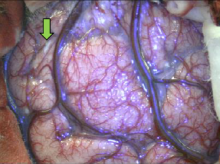
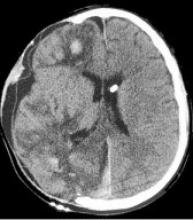
Severe intracranial hypertension treated with 7.5% hypertonic solution in a subarachnoid hemorrhage case by rupture of aneurysm
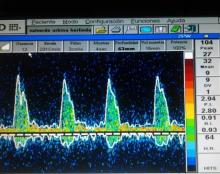
The Transcranial Doppler TCD is a useful tool for the hemodynamic monitoring of the brain when there is cerebral injury due to subarachnoid hemorrhage, it allows us to act in time, since it is a non-invasive tool that is done in the patient's bed.
Aneurysm associated with fenestration of Basilar artery treated by embolization with coils
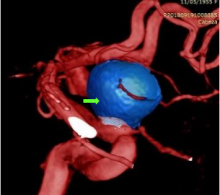
Endovascular treatment with coil Penumbra of a large aneurysm of the right ophthalmic segment
Coiling is the most common endovascular technique used for the treatment of aneurysms. Different types are available and Penumbra coils are a new option in the endovascular armamentarium.
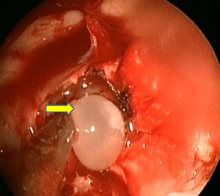
CSF leakage and bone erosion caused by cysts in basal cistern neurocysticercosis treated by endoscopy
Neuroendoscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic method of various forms of neurocysticercosis. Extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis is able to produce bone and dural erosion, so must be considered in the differential diagnosis of cerebrospinal fluid.
First experience using 5-ALA for high grade gliomas in the Almenara Hospital
The infiltrative nature of malignant gliomas make their resection a challenge to neurosurgeons. 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) is a drug that helps to properly delimit the edges of a high-grade glioma, by using a modified microscope, and thus increases the degree of tumor resection, ultimately improving the prognosis of the disease.
Prognostic factors in the survival of patients operated of astrocytoma grade II
Survival of patients operated on Astrocytoma grade II in our hospital is 56.7 months, with the factors of better prognosis being the "low risk" group and the total resection. Its classification into prognostic risk groups based on pre-surgical clinical data helps us predict survival before surgery.
Decompressive Craniectomy in the Management of Refractory PostTraumatic Intracranial Hypertension
Traumatic intracranial hypertension is the major pathophysiological issue of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and its treatment usually demands general and specific measures; nevertheless decompressive craniectomy is an extreme resource available for refractory cases, current data are not enough to define its indications and long term results.They concluded that descompressive craniectomy is a useful option for ICP control and a better outcome of the TBI in the long term.