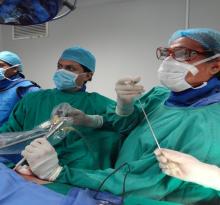
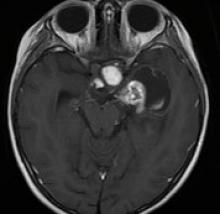
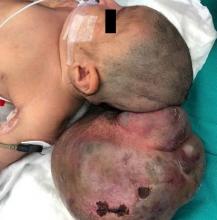
Endovascular treatment with coils of aneurysm of the anterior communicating artery, angiographic control, and evolution according to packing density: case series.
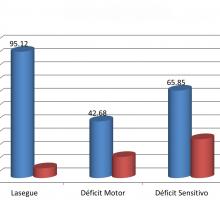
The goal of this study is to present the outcomes of endovascular treatment performed on a group of patients diagnosed with ruptured aneurysms in the anterior communicating artery. The effectiveness of the treatment will be assessed based on the degree of packing observed in both immediate and subsequent angiography control.