Usted está aquí
Peruvian Journal of Neurosurgery
Intraoperative Intracraneal pressure monitoring in decompressive craniectomy for severe TCE
ABSTRACT
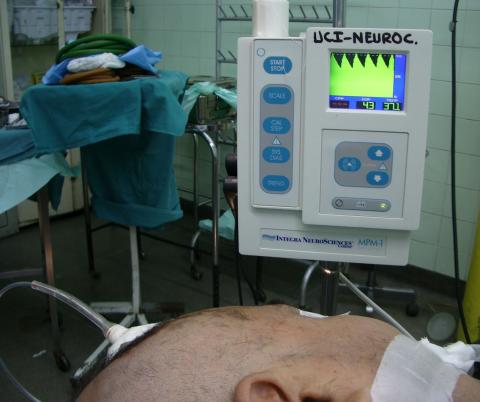
The reduction of intracranial pressure (ICP) is a cornerstone in the management of patients with severe head injury, ICP monitoring remains very important as it helps to optimize treatment and improve prognosis. Decompressive craniectomy (DC) has proved to be an effective method in reducing intracranial pressure when other treatments have failed. ICP monitoring studies in the pre and post operative show that this reduction is immediate and sustained within 48 hours. However, little is known about the variation of the ICP during the performance of decompressive craniectomy and the contribution of each of its stages, as the removal of bone, dural opening and duraplasty in the final result. We report the case of a patient with severe TBI who underwent intracranial pressure monitoring during the performance of decompressive craniectomy in the Guillermo Almenara Hospital in 2009.