Usted está aquí
Peruvian Journal of Neurosurgery
Cerebral aneurysm diagnosed with angio-tomography and its surgical correlation at Daniel A. Carrión Hospital in the period May 2004 to November 2007
ABSTRACT
Objective: To determine the validity, sensitivity and specificity of multislice spiral CT angiography (ATEM) with a 16-Multislice CT scanner detector lines in the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms and their most frequent localizations.
Patients and Methods: We selected 51 patients with nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage due to suspected intracranial aneurysm who underwent surgery in the Hospital Daniel A. Carrión, Callao, for the period May 2004 to November 2007.
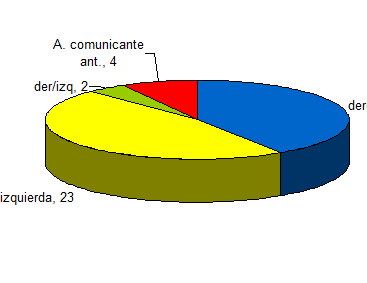
Results: The sensitivity of the ATEM for the detection of intracranial aneurysms in this study was 100%. The resulting specificity was 50%. The positive predictive value (PPV) of ATEM for the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms was 98%, with 87.8% accuracy of the method for determining the location of the aneurysm and 12.2% of uncertainty in the determination of the location of this anomaly. The average size of the aneurysm at surgery was 11.33 + / - 6.9 mm. While the average size of the aneurysm by ATEM was 8.60 + / - 5.75 mm. The difference between the means of these measurements was significant (p = 0.027). 70.3% of aneurysms in this study were found in posterior communicating segment of both internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries both.
Conclusion: CT angiography is an excellent noninvasive test for the detection of intracranial aneurysms and to determine its location.
Key words: Intracranial aneurysm, CT Angio (ATEM), aneurysm surgery