Usted está aquí
Peruvian Journal of Neurosurgery
Radiosurgery in the treatment of brain metastases
ABSTRACT
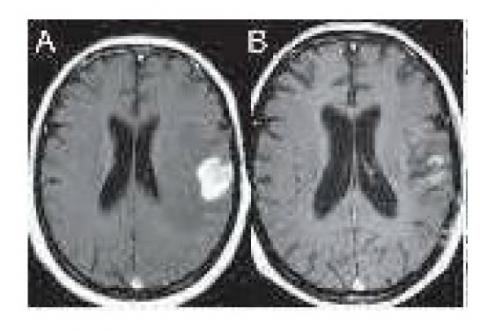
Radiosurgery may be chosen for brain metastases smaller than 3.5 cm. Of large diameter and with the primary tumor controlled in the following scenarios: 1) Solitary metastases and in good neurological conditions could be treated with radiosurgery only 2) Relatively radioresistant metastases such as melanoma and renal cell carcinoma, 3) Multiple metastases, complementing with total brain radiotherapy, 4) Recurrent metastases. The relative indications for radiosurgery alone, radiosurgery, more radiotherapy, radiotherapy alone and surgical resection remain controversial. Because of its proven efficacy and low morbidity, radiosurgery could be indicated for most cases of brain metastases excluding lesions larger than 3.5 cm, numerous metastases (depending on cumulative volume and whole dose to the brain) and / or with symptomatic mass effect, or causing hydrocephalus. In the latter case the surgery would be the first therapeutic consideration and when a biopsy is necessary to confirm a neoplasia.