Usted está aquí
Peruvian Journal of Neurosurgery
Intracranial Solitary Plasmacytoma: Case Report
JORGE ZUMAETA S., MANUEL LAZON A., ANNEL MURGA V.
Abstract (Spanish) ||
Full Text ||
PDF (Spanish) ||
PDF (English)
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Solitary intracranial plasmacytoma is a rare plasma cell tumor that affects the skull, meninges, and brain. Unlike multiple myeloma, it does not have systemic manifestations. Its symptoms are characterized by a progressively growing tumor that generates local pain. It does not have a pathognomonic image and can be confused with other lesions, being its diagnosis histological. The prognosis is good and the main treatment modalities are surgery and/or radiation therapy.
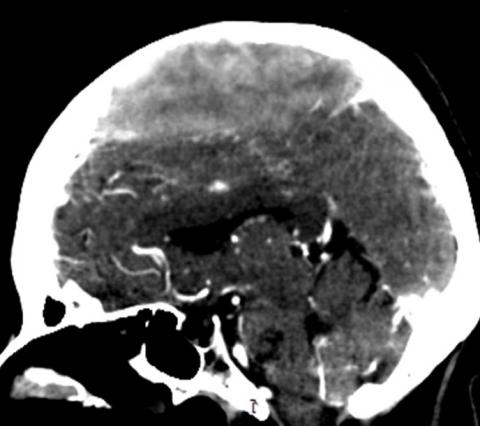
Clinical Case: 64-year-old female patient with a clinical picture characterized by loss of strength in lower limbs and thermal rise. On examination: Patient awake, Glasgow 15 points, paraparesis 4/5, photoreactive and isochoric pupils. Imaging examinations show an extensive contrast-enhancing lesion involving cerebral meninges at the frontoparietal level bilaterally, with a moderate mass effect. A subtotal resection of the lesion is performed, with the patient presenting a good clinical evolution. The histological result was a plasma cell tumor. In the 6-month follow-up, no residual lesion was observed, maintaining outpatient control by an outpatient clinic. This case shows a rare pathology that is sometimes confused with a meningioma.
Conclusion: Solitary intracranial plasmacytoma is a rare tumor that can easily be confused with other more common lesions. Its diagnosis is only made with a histological study. It has a good prognosis and can be treated by surgical resection and/or radiotherapy.
Keywords: Plasmacytoma, Brain, Meninges, Neoplasms, Plasma Cell (Source: MeSH NLM)