Usted está aquí
Peruvian Journal of Neurosurgery
Surgical treatment of Pituitary Adenoma: Results in a series of 403 patients
ABSTRACT
Objective: Pituitary adenomas are benign tumors that occur in approx. 10 to 15% of all intracranial tumors. Treatment can be carried by transsphenoidal resection (TSR) or transcranial resection (TCR). The aim of this study is to present the results of surgical treatment in a series of 403 patients operated at the Almenara Hospital between 2000 and 2008.
Patients and Methods: We performed a retrospective descriptive study of patients operated on pituitary adenomas from January 2000 to December 2008. It were reviewed medical records and operative reports, and gathered data on sex, age, type of adenoma, type of approach, complications, recurrence and mortality.
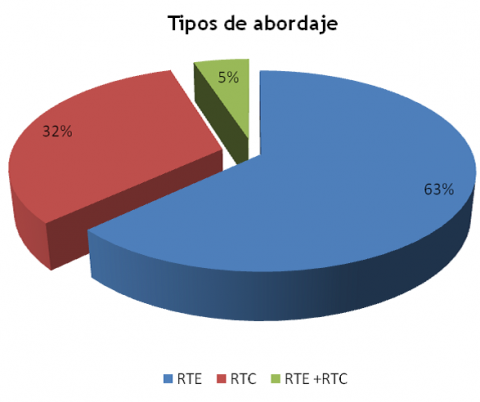
Results: 403 patients were operated of which 51% were female and 49% men. The most affected age group was 50-59 years (24.3%) followed by 40-49 years (21.2%). The most common type of adenoma was the normally functioning (60.5%). Transsphenoidal approach was used in 63%, followed by transcranial (32%) and combined (5%). TSR predominated in ACTHproducing adenomas (89%), while the TCR in prolactin-producing (70%). The most common complication was transient diabetes insipidus (50.1%). The recurrence rate was 12.9% being more frequent in the ACTH-producing tumor (21.6%) and the mortality rate was 5.2% with higher frequency in the TCR (7.0%)
Conclusions: The transsphenoidal approach the method of choice in the vast majority of pituitary tumors. The transcranial approach has specific indications and should be reserved for cases of difficult access by transsphenoidal. The adoption of new techniques, proper equipment, training and multidisciplinary working are essential to further decrease complications and mortality.