Usted está aquí
Peruvian Journal of Neurosurgery
Neurosurgical treatment of unstable cervical spine due to rheumatoid arthritis: case series
JORGE ZUMAETA S, ELAR CARI C, ALFONSO BASURCO C, CESAR POLO D, JESUS CABREJOS B, PABLO PINO L, JUAN SALAS G, EDUARDO LAOS P, ROBERT BURGOS C.
Abstract (Spanish) ||
Full Text ||
PDF (Spanish) ||
PDF (English)
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic disease characterized by synovitis, which causes damage to the ligaments and joints. The cervical region is the region of the spine most affected, with neck pain the most frequent symptom. The three forms of presentation are atlantoaxial subluxation, cranial settlement, and subaxial subluxation. The clinical evolution of patients treated conservatively is poor, with surgery being a key element to prevent the progression of neurological deterioration.
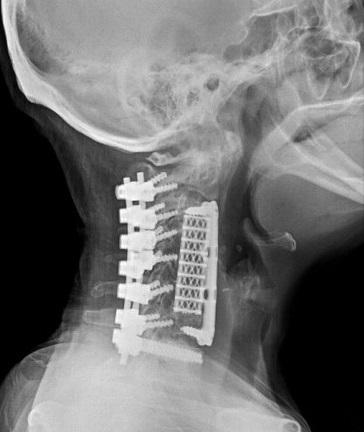
Methods: A retrospective study of 10 patients with RA operated between 2015 and 2019 was carried out. Ranawat criteria were used for clinical classification and imaging studies were performed to confirm cervical instability. Anterior and posterior cervical arthrodesis techniques were used. Control after surgery was performed by tomography and the Ranawat score was determined in the outpatient control.
Results: In the period 2015 and 2019, 10 patients with RA who presented symptoms of cervical instability were operated on. All patients were female, aged between 52 and 73 years. The most frequent symptom was neck pain. Most of the patients presented inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP) in high values. The most frequent cervical involvement was atlantoaxial instability. The most common surgical technique used was posterior C1-C2 arthrodesis via the inter-articular approach. Ranawat's classification improved in 90% of patients after surgery. Complications were surgical site infections and rupture of occipitocervical fixation bars, which were adequately resolved.
Conclusions: Surgery for patients with vertebral instability due to RA should be aimed at treating intractable pain and stopping the progression of cervical instability, with the aim of promoting neurological recovery and reducing mortality.
Keywords: Spine, Arthritis, Rheumatoid, Joint Instability, Synovitis, Neck Pain, Arthrodesis. (source: MeSH NLM)