Surgical Treatment of Traumatic brain injury: Results in a series of 76 patients
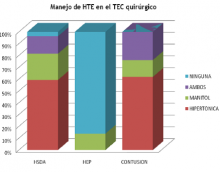
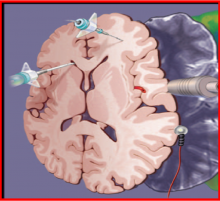
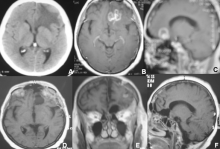
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality mainly in young people, and also one of the most common neurosurgical diseases in daily practice. Medical and surgical optimal treatment are essential to achieving shorter hospital stay, good Glasgow scale and GOS, reduce complications and mortality rate.The aim of this study is to present the results in 76 patients operated on at Almenara Hospital in 2008 and 2009.