Decompressive Craniectomy in the Management of Refractory PostTraumatic Intracranial Hypertension
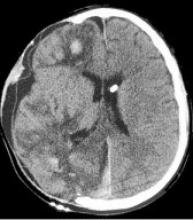
Traumatic intracranial hypertension is the major pathophysiological issue of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and its treatment usually demands general and specific measures; nevertheless decompressive craniectomy is an extreme resource available for refractory cases, current data are not enough to define its indications and long term results.They concluded that descompressive craniectomy is a useful option for ICP control and a better outcome of the TBI in the long term.